Regardless of where you stand on the vaccine debate, my goal is to provide reliable, fact-based information on current vaccine trends and to share the good news about the powerful role herbal medicine, nutrition, and diet play in building a healthy immune system. There is undoubtedly a great deal of conflicting misinformation circulating in the public amidst a high degree of vaccine skepticism. On a positive note, the latest scientific consensus is now confirming a reduced rate of severe illness and death from COVID-19, including the Delta variant, in vaccinated individuals, especially for high-risk populations, including the elderly and those with underlying conditions. A recent meta-analysis on Vitamin D is also garnering attention on the critical importance of this nutrient. However, with vaccine effectiveness waning[1],[2] amidst rising numbers of breakthrough infections, the continued transmissibility of infection despite vaccination[3], and new variants of concern continuing to emerge[4], the challenge of relying exclusively on immunizations to move past the pandemic underscores the importance of being ever more vigilant in optimizing our health.
Promising Clinical Trial Results on the New, Upcoming Novavax Vaccine
Clinical data from studies of the Novavax (NVX-CoV2373) vaccine, a recombinant nanoparticle vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 that contains the full-length spike glycoprotein of the prototype strain plus Matrix-M adjuvant, showed that the vaccine was safe and associated with a robust immune response in healthy adult participants. Matrix-M adjuvant, is a plant derived saponin, from the inner bark of Quillaja saponaria, the Chilean soap bark tree which is added to augment clinically significant antibody and T-cell responses to the vaccine antigen against the virus.[5]
The results of a recent clinical trial that involved a total of 15,187 participants that underwent randomization, and 14,039 were included in the per-protocol efficacy population, found that a two-dose regimen of the Novavax vaccine administered to adult participants conferred 90% protection against SARS-CoV-2 infection and showed high efficacy against the Delta (B.1.1.7) variant. The incidence of serious adverse events was low and similar in the two groups.[6]
Early trials on the Novavax vaccine showed that a two-dose regimen administered 21 days apart was safe and associated with a robust immune response in healthy adult participants.[7],[8]
Vaccine Effectiveness Against the Delta Variant
“Two days after my first symptoms, I began to feel seriously ill,” wrote BBC TV presenter Andrew Marr.[9] He described how he had previously felt invulnerable having received both of his Covid vaccine doses. Nonetheless, he became infected with the virus. Marr recovered but some have not. Data from Public Health England reveals that of all the people who died within 28 days of testing positive for the Delta variant between February 1, 2021, and July 19, 2021, 49% (224) had had two vaccine doses. Almost all these people, 220, were aged 50 or older.[10]
According to a large English coronavirus prevalence study[11] vaccinated people have an approximately 50% reduced risk of infection from the Delta coronavirus variant, including those who are asymptomatic. In this study researchers from Imperial College London reported that people who received two vaccine doses were half as likely to test positive for COVID-19, adjusting for other factors such as age, and whether the people tested had COVID-19 symptoms.
Studies by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention say the delta infection has similarly high viral loads in vaccinated and unvaccinated people.[12]
Data published by the Israeli government suggests that the Pfizer BioNTech vaccines efficacy against symptomatic infection fell from 94% to 64% after the Delta variant began spreading in the country.[13] The United States has announced plans to offer booster shots to all Americans, citing data showing diminishing protection. Canada, France, and Germany will be doing the same.
Fighting an outbreak of the Delta variant since June of this year, Israel presently has one of the world’s highest infection rates per capita. Close to 1.5 million people out of the country’s 9.3 million population have taken a third shot. Ministry officials from Israel’s Gertner Institute and KI Institute, said that among people aged 60 and over, the protection against infection provided from 10 days after a third dose was four times higher than after two doses. Regarding serious illness and hospitalization, a third booster shot for over 60-year-olds offered five to six times greater protection after 10 days.[14]
The good news regarding vaccines is that according to vaccines in use in the UK (Pfizer BioNtech, AstraZeneca, and Moderna), all reduce the risk of death by more than 85%, regardless of variant.
According to a recent (not yet peer reviewed) observational study from Mayo Clinic that compared the Pfizer BioNTech and Moderna vaccines effectiveness against breakthrough infections and severity of disease during periods of Alpha and Delta variant prevalence from January 2021 thru July 2021, as the Delta variant prevalence increased, vaccine effectiveness was considerably lower for both vaccines. The study also conferred a two-fold risk reduction against breakthrough infection with Moderna’s vaccine compared to the Pfizer BioNTech vaccine.[15]
A grim warning from Israel was that almost 60% of Covid hospitalizations are in the fully vaccinated. “Now is a critical time,” Israeli Minister of Health Nitzan Horowitz said as the 56-year-old got a COVID-19 booster shot on August 13th , 2021, the day his country became the first nation to offer a third dose of vaccine to people as young as age 50. “We’re in a race against the pandemic.”
His message was meant for his fellow Israelis, but it is a warning to the world. Israel has among the world’s highest levels of vaccination for COVID-19, with 78% of those 12 and older fully vaccinated, the vast majority with the Pfizer vaccine. Yet the country is now logging one of the world’s highest infection rates, with nearly 650 new cases daily per million people. More than half are in fully vaccinated people, underscoring the extraordinary transmissibility of the Delta variant and stoking concerns that the benefits of vaccinations ebb over time.
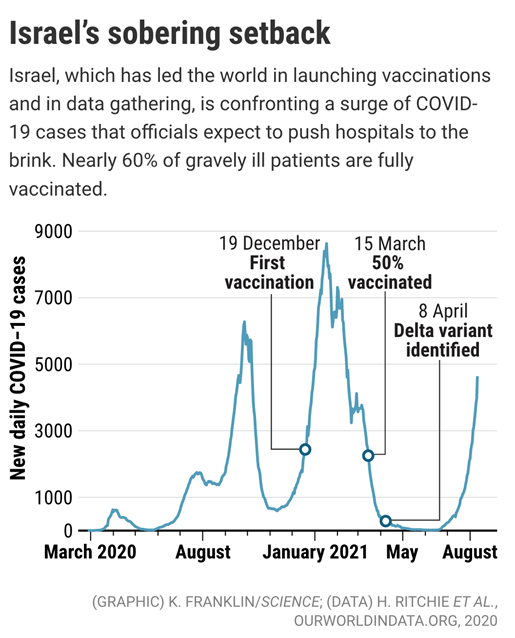
As of August 15th , 2021, 514 Israelis were hospitalized with severe or critical COVID-19, a 31% increase from just 4 days earlier. Of the 514, 59% were fully vaccinated. Of the vaccinated, 87% were 60 or older. “There are so many breakthrough infections that they dominate and most of the hospitalized patients are actually vaccinated,” says Uri Shalit, a bioinformatician at the Israel Institute of Technology (Technion) who has consulted on COVID-19 for the government.[16]
Fighting an outbreak of the Delta variant since June, 2021, Israel presently has one of the world’s highest infection rates per capita. Close to 1.5 million people out of the country’s 9.3 million population have taken a third shot. Ministry officials from Israel’s Gertner Institute and KI Institute, said that among people aged 60 and over, the protection against infection provided from 10 days after a third dose was four times higher than after two doses. Regarding serious illness and hospitalization, a third booster shot for over 60-year-olds offered five to six times greater protection after 10 days[17]
Why the Current Vaccines Aren’t Working As Well As You Think against the Delta Variant And Most Likely Future Mutations
Several of the virus mutants that emerged had evolved spike proteins in which the segments targeted by the antibodies had changed, allowing these mutant viruses to remain undetected. An analysis of more than 50,000 real-life SARS-CoV-2 genomes isolated from patient samples further showed that most of these virus mutations were already circulating, albeit at very low levels in the infected human populations. These results confirm that SARS-CoV-2 can mutate its spike proteins to evade antibodies, and that these mutations are already present in some virus mutants circulating in the human population.[18] All vaccines that are deployed on a large scale should be designed to activate the strongest possible immune response against more than one target region on the spike protein, as more and more mutations occur.
Outbreak of SARS-CoV-2 Infections, Including COVID-19 Vaccine Breakthrough Infections
A recently released report from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention suggests that the viral load of vaccinated people infected with the Delta variant is similar to that of unvaccinated people. This study began on July 3rd, 2021, in Provincetown, Massachusetts and involved 469 cases. Massachusetts has a high rate of vaccination at 69% among eligible adults at the time of the study. It found that three-quarters of cases occurred in fully vaccinated people. It found no significant difference in the viral load present in the breakthrough infections occurring in fully vaccinated people and the other cases.[19]
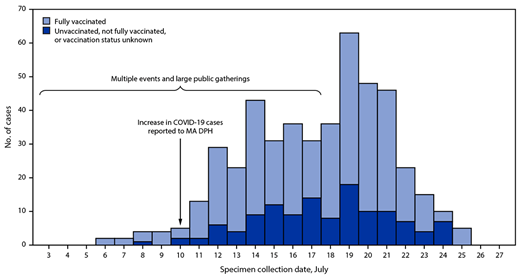
Abbreviation: MA DPH = Massachusetts Department of Public Health.
* Fully vaccinated was defined as ≥14 days after completion of state immunization registry–documented COVID-19 vaccination as recommended by the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices.
Meanwhile, in Israel, the health ministry released a paper on July 5th, 2021, suggesting that with the rise of the Delta variant in the nation, the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine was now 64% effective against infection or symptomatic illness, but still 93% effective in preventing serious illness and hospitalization. However, in late July, 2021 the ministry further reduced its vaccine effectiveness estimate for symptomatic COVID-19 to 40.5%, but once again, found protection against severe disease to remain robust — 88.0% effective against hospitalization and 91.4% effective against severe COVID-19.[20]
A study from China, posted as a preprint on July 12th , 2021, found that the concentration of viral particles — a proxy for infectiousness — in people infected with the Delta variant was roughly 1,000 times that in people infected with the original strain of SARS-CoV-2.[21]
Reports on A New Variant of Concern
Data from the second week of July, 2021 reveals that 63 percent of a sampling of COVID-19 patients in Jackson Memorial Health System and at University of Miami’s UHealth Tower had the highly transmissible form of the virus. This sequencing data also revealed that 20 percent of patients had the Brazilian variant (now known as Gamma), 9 percent had the Colombian variant (B.1.621), which is dominating that country, and 3 percent had the Lambda variant that is currently the dominant COVID-19 strain in Peru. Dr. David Andrews states “The Colombian variant and the Lambda variant share many of the properties of the other bad players we have seen emerging—like Delta—such as increased transmissibility and a potential to escape the immunity provided by vaccines,” said Dr. David Andrews, Associate Professor in the Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, who is leading the University’s effort to sequence COVID-19 positive samples.[22]
The Debate Concerning Natural Immunity
For over a year, mainstream media, health authorities as well as many “experts” have been downplaying the power of the immune system, dismissing natural immunity and proclaiming that immunity to COVID-19 was short-lived.
The study[23] that the CDC is referring to when it states vaccine immunity is superior to natural immunity is terribly flawed. Let me give you a direct quote from the full paper itself and then you can judge if this study proves anything:
“The lack of a significant association with partial versus full vaccination should be interpreted with caution given the small numbers of partially vaccinated persons included in the analysis (6.9% of case-patients and 7.9% of controls), which limited statistical power.
The findings in this report are subject to at least five limitations:
- Reinfection was not confirmed through whole genome sequencing, which would be necessary to definitively prove that the reinfection was caused from a distinct virus relative to the first infection. Although in some cases the repeat positive test could be indicative of prolonged viral shedding or failure to clear the initial viral infection, given the time between initial and subsequent positive molecular tests among participants in this study, reinfection is the most likely explanation.
- Persons who have been vaccinated are possibly less likely to get tested. Therefore, the association of reinfection and lack of vaccination might be overestimated.
- Vaccine doses administered at federal or out-of-state sites are not typically entered in KYIR, so vaccination data are possibly missing for some persons in these analyses. In addition, inconsistencies in name and date of birth between KYIR and NEDSS might limit ability to match the two databases. Because case investigations include questions regarding vaccination, and KYIR might be updated during the case investigation process, vaccination data might be more likely to be missing for controls. Thus, the OR might be even more favorable for vaccination.
- Although case-patients and controls were matched based on age, sex, and date of initial infection, other unknown confounders might be present.
- Finally, this is a retrospective study design using data from a single state during a 2-month period; therefore, these findings cannot be used to infer causation. Additional prospective studies with larger populations are warranted to support these findings.”
Natural Immunity Offers Durable Protection Superior to Vaccines
Citing very preliminary data, those who recovered from COVID-19 may be better protected from reinfection than those who received the vaccine. Since May 1st, 2021, 72 people who previously had COVID were infected again, accounting for 1 percent of confirmed new cases, while 3,000 who were vaccinated have been infected — 40% of confirmed new cases.[24]
Dr. Ryan Cole, a Mayo Clinic trained Board-Certified Pathologist who runs his own private diagnostic laboratory, is perhaps one of the most qualified physicians in America today to give an independent, honest evaluation. He explained that natural immunity produces broad immunity that can’t be matched by vaccination. “A natural infection induces hundreds upon hundreds of antibodies against all proteins of the virus, including the envelope, the membrane, the nucleocapsid, and the spike,” said Dr. Cole, who has spent the past 16 months examining and culturing SARS-CoV-2 specimens. “Dozens upon dozens of these antibodies neutralize the virus when encountered again. Additionally, because of the immune system exposure to these numerous proteins (epitomes), our T cells mount a robust memory, as well. Our T cells are the ‘marines’ of the immune system and the first line of defense against pathogens. T-cell memory to those infected with SARS-CoV1 is at 17 years and running still.” In vaccine-induced immunity, we mount an antibody response to only the spike and its constituent proteins. This produces much fewer neutralizing antibodies, and “as the virus preferentially mutates at the spike, these proteins are shaped differently, and antibodies can no longer ‘lock and key’ bind to these new shapes.”[25]
Numerous scientists have found those with natural immunity have a decreased risk of re-infection[26],[27] and extremely low rates of hospitalization and death due to a repeat infection.
Epidemiologists estimate over 160 million people worldwide[28] have recovered from COVID-19. Those who have recovered have an astonishingly low frequency of repeat infection, disease, or death. The World Health Organization (WHO) released a scientific update stating[29] that most people who have recovered from COVID-19 develop robust protective immunity. Importantly, they summarize that within four weeks of infection, 90% to 99% of people who recover from COVID-19 develop detectable neutralizing antibodies.[30],[31],[32]
A study in the UK reported in The Lancet, called the SARS-CoV-2 Immunity and Reinfection Evaluation (SIREN) study, suggests that being seropositive to SARS-CoV-2 through natural infection protects robustly from asymptomatic and symptomatic reinfection.[33]
Although antibodies induced by SARS-CoV-2 infection are more variable and often lower in titre (titer) than antibody responses induced after vaccination, this observation does make sense considering current SARS-CoV-2 vaccines induce systemic immune responses to spike proteins, while natural infection also induces mucosal immune responses and immune responses against the many other open reading frames encoded by the approximately 29,900 nucleotides of SARS-CoV-2. There is a growing number of studies which demonstrate that infection does protect against reinfection, and probably in an antibody-dependent manner.[34],[35],[36],[37],[38]
In Qatar, a study found that there is “no evidence of waning of immunity for over seven months of the follow-up period.” Reinfections that did occur were “less severe than primary infections.” We obviously need more studies, but it certainly appears that patients who had a natural infection may have garnered more protection against the virus.[39]
A study[40] that followed 254 COVID-19 patients for up to 8 months concluded that they had “durable broad-based immune responses.” In fact, even very mild COVID-19 infection also protected the patients from an earlier version of the “SARS” coronavirus that first emerged around 2003, and against COVID-19 variants. “Taken together, these results suggest that broad and effective immunity may persist long-term in recovered COVID-19 patients,” concludes the study scientists.
Another study[41] followed 52,238 employees of the Cleveland Clinic Health System in Ohio, and found that for previously infected people, the cumulative incidence of reinfection “remained almost zero.” According to the study, “Not one of the 1,359 previously infected subjects who remained unvaccinated had a COVID-19 infection over the duration of the study” and vaccination did not reduce the risk. “Individuals who have had the COVID-19 infection are unlikely to benefit from the COVID-19 vaccination,” concludes the study scientists.
A 2020 study[42] reported that people who had recovered from SARS-CoV — a virus that is genetically similar to SARS-CoV-2 and belongs to the same viral species — maintained significant levels of neutralizing antibodies at least 17 years after initial infection.
More Vitamin D Updates and This Time It Appears to Even Protect against Getting COVID-19
Several studies have shown an association between low vitamin D levels and increased risk for COVID-19, though not a direct link. One paper from Meltzer and his colleagues published in September 2020, found that people who were vitamin D-deficient were more likely to test positive for COVID-19.[43]
Another more recent study found that black individuals who have higher levels of vitamin D were less likely to test positive for COVID-19 than people with sufficient levels. This study, published in JAMA Open Network on March 19, retrospectively examined the relationship between vitamin D levels and the likelihood of testing positive for COVID-19. While levels of 30 ng/ml of 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25OHD) or more are usually considered sufficient, the authors found that black individuals who had levels of 30 to 40 ng/ml 25OHD had a 2.64 times higher risk of testing positive for COVID-19 than people with levels of 40 ng/ml or greater.[44]
A recent study also found that more than 80% of patients diagnosed with COVID-19 were vitamin D deficient. 25OHD levels are lower in hospitalized COVID-19 patients than in population-based controls and these patients had a higher prevalence of deficiency. Vitamin D-deficient COVID-19 patients had a greater prevalence of hypertension and cardiovascular diseases, as well as a longer length of hospital stay than those with serum 25OHD levels ≥20 ng/mL.[45]
Vitamin D Appears to Prevent and Treats Viral Respiratory Tract Infections, According to a Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials
Viral respiratory tract infections (RTIs) have been recognized as a global public health burden. Despite current theories about their effectiveness, the true benefits of dietary supplements on the prevention and treatment of viral RTIs remain elusive. This study systematically searched databases of PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, and Google Scholar through March 4, 2020, to identify randomized controlled trials that evaluated the effects of consuming selected dietary supplements on the prevention or treatment of viral RTIs. Thirty-nine randomized controlled trials (n = 16,797 participants) were eligible and included.
The conclusion of this meta-analysis study found that vitamin D supplementation improved viral RTIs across cohorts particulate in those with vitamin D deficiency.[46]
A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Vitamin D and COVID-19 Patient Outcome
PubMed/MEDLINE, Scopus, and Web of Science databases were systematically searched using appropriate keywords till June 8, 2021, to identify observational studies and randomized controlled trials (RCTs) reporting adverse clinical outcomes (ICU admission and/or mortality) in COVID-19 patients receiving vitamin D supplementation vs. those not receiving the same. Both prior use and use of vitamin D after COVID-19 diagnosis were considered.
13 studies (10 observational, 3 RCTs) were identified, and the pooled results showed that:
- Vitamin D use in COVID-19 was significantly associated with reduced ICU admission/mortality.
- Vitamin D was also found to reduce the risk of adverse outcomes.
- Vitamin D supplementation was associated with improved clinical outcomes only in patients receiving the drug post-COVID-19 diagnosis and not in those who had received vitamin D before diagnosis.
In conclusion, the present systematic review and meta-analysis suggests that vitamin D supplementation appears be associated with improved clinical outcomes in terms of ICU admission and/or mortality, especially in those with moderate-to-severe COVID-19 requiring hospitalization.[47]
Poor Outcomes in COVID-19 Patients with Zinc Deficiency
Zinc is a trace element with potent immunoregulatory and antiviral properties and is utilized in the treatment of COVID-19.
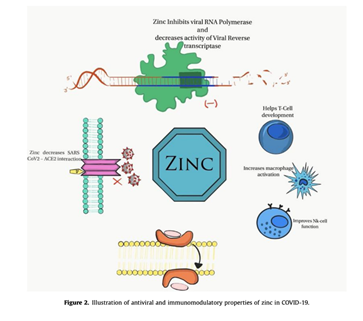
This study was a prospective study of fasting zinc levels in COVID-19 patients at the time of hospitalization. An initial comparative analysis was conducted between COVID-19 patients and healthy controls. COVID-19 patients with zinc deficiency were compared to those with normal zinc levels.
COVID-19 patients (n = 47) showed significantly lower zinc levels when compared to healthy controls (n = 45): median 74.5 (interquartile range 53.4-94.6) μg/dl vs 105.8 (interquartile range 95.65-120.90) μg/dl (p < 0.001).
Amongst the COVID-19 patients, 27 (57.4%) were found to be zinc deficient.
Zinc deficient patients were found to have higher rates of complications:
- acute respiratory distress syndrome (18.5% vs 0%, p = 0.06),
- corticosteroid therapy (p = 0.02),
- prolonged hospital stay (p = 0.05), and
- increased mortality (18.5% vs 0%, p = 0.06).
The odds ratio (OR) of developing complications was almost 6x higher for zinc deficient COVID-19 patients.
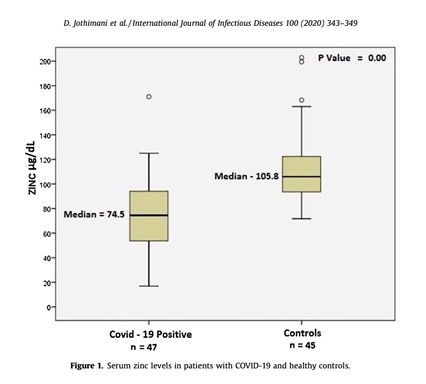
The study data clearly show that a significant number of COVID-19 patients were zinc deficient. These zinc deficient patients developed more complications, and the deficiency was associated with a prolonged hospital stay and increased mortality.[48]
I can’t emphasize enough the importance of normalizing your vitamin D, zinc, and magnesium levels, as well as eating an abundance of whole foods such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, pre and probiotic foods, and legumes, such as lentils.[49] In previous blogs I have shared various specific herbal remedies used in traditional medicine for viral infections and immune health (see https://www.donnieyance.com/herbal-remedies-for-acute-viral-infections/). There is still so much we need to know and will come to learn about COVID-19 over time. Let’s keep an open mind and continue to seek the truth and be respectful of others whose thoughts, feelings, and opinions may differ from those of our own.
In the spiritual mindset, “heart” refers to the mind, will, and emotions and is closely tied to the pursuit of truth and holiness, along with the desire for goodness; which requires us be open and pray. Then you will find “The truth (and it) will set you free'” (John 8:32)
[1] Callaway E, Delta coronavirus variant: scientists brace for impact. https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-021-01696-3 Date: June 22, 2021, Date accessed: July 12, 2021
[2] Vasileiou E, Simpson CR, Shi T, et al. Interim findings from first-dose mass COVID-19 vaccination roll-out and COVID-19 hospital admissions in Scotland: a national prospective cohort study. Lancet. 2021; 397: 1646-1657
[3] Baraniuk C. Covid-19: How effective are vaccines against the delta variant? BMJ. 2021 Aug 9;374:n1960. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n1960. PMID: 34373255.
[4] Campbell F, Archer B, Laurenson-Schafer H et al. Increased transmissibility and global spread of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern as at June 2021. Euro Surveill. 2021; 262100509
[5] Ragupathi G, Gardner JR, Livingston PO, Gin DY. Natural and synthetic saponin adjuvant QS-21 for vaccines against cancer. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2011;10(4):463-470. doi:10.1586/erv.11.18
[6] Heath PT, Galiza EP, Baxter DN, Boffito M, Browne D, Burns F, Chadwick DR, Clark R, Cosgrove C, Galloway J, Goodman AL, Heer A, Higham A, Iyengar S, Jamal A, Jeanes C, Kalra PA, Kyriakidou C, McAuley DF, Meyrick A, Minassian AM, Minton J, Moore P, Munsoor I, Nicholls H, Osanlou O, Packham J, Pretswell CH, San Francisco Ramos A, Saralaya D, Sheridan RP, Smith R, Soiza RL, Swift PA, Thomson EC, Turner J, Viljoen ME, Albert G, Cho I, Dubovsky F, Glenn G, Rivers J, Robertson A, Smith K, Toback S; 2019nCoV-302 Study Group. Safety and Efficacy of NVX-CoV2373 Covid-19 Vaccine. N Engl J Med. 2021 Jun 30:NEJMoa2107659. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2107659. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 34192426; PMCID: PMC8262625.
[7] Keech C, Albert G, Cho I, et al. Phase 1-2 trial of a SARS-CoV-2 recombinant spike protein nanoparticle vaccine. N Engl J Med 2020; 383: 2320-32.
[8] Formica N, Mallory R, Albert G, et al. Evaluation of a SARS-CoV-2 vaccine NVX-CoV2373 in younger and older adults. March 1, 2021 (https://www .medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.02.26.21252482v1).
[9]Marr A. Marr on catching Covid after being double vaccinated. 28 June 2021. www.bbc.co.uk/news/health-57640550.
[10] Public Health England. Investigation of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern: technical briefings. 23 July 2021. www.gov.uk/government/publications/investigation-of-novel-sars-cov-2-variant-variant-of-concern-20201201.
[11] Study finds 50%-60% reduced risk of Covid-19 for fully vaccinated Read more at: https://www.deccanherald.com/science-and-environment/study-finds-50-60-reduced-risk-of-covid-19-for-fully-vaccinated-1016026.html
Reuters, London, AUG 04 2021, 06:54 ISTUPDATED: AUG 04 2021, 16:55 IS
Read more at: https://www.deccanherald.com/science-and-environment/study-finds-50-60-reduced-risk-of-covid-19-for-fully-vaccinated-1016026.html
[12] https://www.cdc.gov/media/releases/2021/s0730-mmwr-covid-19.html, Statement from CDC Director Rochelle P. Walensky, MD, MPH on Today’s MMWR, retrieved August 20, 2021
[13] Odenheimer A, Shepherd D. Pfizer shot halts severe illness in Israel as delta spreads. Bloomberg. 5 July 2021. www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2021-07-05/israel-sees-decline-in-pfizer-vaccine-efficacy-rate-ynet-says.
[15] Arjun Puranik, Patrick J. Lenehan, Eli Silvert, Michiel J.M. Niesen, Juan Corchado-Garcia, John C. O’Horo, Abinash Virk, Melanie D. Swift, John Halamka, Andrew D. Badley, A.J. Venkatakrishnan, Venky Soundararajan, Comparison of two highly-effective mRNA vaccines for COVID-19 during periods of Alpha and Delta variant prevalence
medRxiv 2021.08.06.21261707; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.08.06.21261707
[16] doi:10.1126/science.abl9630, A grim warning from Israel: Vaccination blunts, but does not defeat Delta, By Meredith Wadman Aug. 16, 2021 , 6:55 PM, https://www.sciencemag.org/news/2021/08/grim-warning-israel-vaccination-blunts-does-not-defeat-delta
[17] Israel finds COVID-19 vaccine booster significantly lowers infection risk, https://www.reuters.com/world/middle-east/israel-finds-covid-19-vaccine-booster-significantly-lowers-infection-risk-2021-08-22/, August 23, 20217:08 AM PDTLast Updated 37 minutes ago
[18] Weisblum Y, Schmidt F, Zhang F, DaSilva J, Poston D, Lorenzi JC, Muecksch F, Rutkowska M, Hoffmann HH, Michailidis E, Gaebler C, Agudelo M, Cho A, Wang Z, Gazumyan A, Cipolla M, Luchsinger L, Hillyer CD, Caskey M, Robbiani DF, Rice CM, Nussenzweig MC, Hatziioannou T, Bieniasz PD. Escape from neutralizing antibodies by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein variants. Elife. 2020 Oct 28;9:e61312. doi: 10.7554/eLife.61312. PMID: 33112236; PMCID: PMC7723407.
[19] Brown CM, Vostok J, Johnson H, et al. Outbreak of SARS-CoV-2 Infections, Including COVID-19 Vaccine Breakthrough Infections, Associated with Large Public Gatherings — Barnstable County, Massachusetts, July 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2021;70:1059-1062. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7031e2
[20] https://www.gov.il/BlobFolder/reports/vaccine-efficacy-safety-follow-up-committee/he/files_publications_corona_two-dose-vaccination-data.pdf retrieved 08/05/2021
[21] Li, B. et al. Viral infection and transmission in a large, well-traced outbreak caused by the SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant, Preprint at https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.07.07.21260122 (July 23, 2021).
[22] https://medicalxpress.com/news/2021-08-evidence-covid-delta-variant-rapidly.html, New evidence shows the COVID-19 delta variant rapidly rising, AUGUST 2, 2021, by University of Miami Health System, Miller School of Medicine
[23] Alyson M. Cavanaugh, DPT, PhD; Kevin B. Spicer, MD, PhD; Douglas Thoroughman, PhD; Connor Glick, MS; Kathleen Winter, PhD, Reduced Risk of Reinfection with SARS-CoV-2 After COVID-19 Vaccination — Kentucky, May–June 2021, Weekly / August 13, 2021 / 70(32);1081-1083
https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7032e1.htm
[24] https://www.timesofisrael.com/liveblog_entry/are-recovered-covid-patients-more-protected-than-the-vaccinated/
[25] https://odysee.com/@SaveMedia:5/capitol-clarity-ryan-cole-on-covid-19-vitamin-d-vaccine-concerns:2
[26] Hall VJ, Foulkes S, Charlett A, Atti A, Monk EJM, Simmons R, Wellington E, Cole MJ, Saei A, Oguti B, Munro K, Wallace S, Kirwan PD, Shrotri M, Vusirikala A, Rokadiya S, Kall M, Zambon M, Ramsay M, Brooks T, Brown CS, Chand MA, Hopkins S; SIREN Study Group. SARS-CoV-2 infection rates of antibody-positive compared with antibody-negative health-care workers in England: a large, multicentre, prospective cohort study (SIREN). Lancet. 2021 Apr 17;397(10283):1459-1469. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00675-9. Epub 2021 Apr 9.
[27] Krammer F. Correlates of protection from SARS-CoV-2 infection. Lancet. 2021 Apr 17;397(10283):1421-1423. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00782-0. Epub 2021 Apr 9. PMID: 33844964; PMCID: PMC8040540.
[28] https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html, retrieved 08/02/2021
[29] COVID-19 natural immunity WHO, 05/2021, https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/341241/WHO-2019-nCoV-Sci-Brief-Natural-immunity-2021.1-eng.pdf?sequence=3&isAllowed=y
[30] Wajnberg A, Mansour M, Leven E, et al. Humoral response and PCR positivity in patients with COVID-19 in the New York City region, USA: an observational study. Lancet Microbe [Internet] 2020 [cited 2021 Mar 26];1(7):e283–9. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2666524720301208
[31] Arkhipova-Jenkins I, Helfand M, Armstrong C, et al. Antibody Response After SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Implications for Immunity : A Rapid Living Review. Ann Intern Med 2021.
[32] Wu J, Liang B, Chen C, et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection induces sustained humoral immune responses in convalescent patients following symptomatic COVID-19. Nat Commun 2021;12(1):1813.
[33] Hall VJ, Foulkes S, Charlett A. SARS-CoV-2 infection rates of antibody-positive compared with antibody-negative health-care workers in England: large, multicentre, prospective cohort study (SIREN) Lancet. 2021 doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00675-9. published online April 9.
[34] Pilz S, Chakeri A, Ioannidis JP. SARS-CoV-2 re-infection risk in Austria. Eur J Clin Invest. 2021;51
[35] Lumley SF, O’Donnell D, Stoesser NE. Antibody status and incidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection in health care workers. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:533–540.
[36] Letizia AG, Ge Y, Vangeti S. SARS-CoV-2 seropositivity and subsequent infection risk in healthy young adults: a prospective cohort study. medRxiv. 2021 doi: 10.1101/2021.01.26.21250535. published online Jan 29.
[37] Sheehan MM, Reddy AJ, Rothberg MB. Reinfection rates among patients who previously tested positive for COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study. medRxiv. 2021 doi: 10.1101/2021.02.14.21251715. published online Feb 16
[38] Hansen CH, Michlmayr D, Gubbels SM, Mølbak K, Ethelberg S. Assessment of protection against reinfection with SARS-CoV-2 among 4 million PCR-tested individuals in Denmark in 2020: a population-level observational study. Lancet. 2021;397:1204–1212
[39] Abu-Raddad LJ, Chemaitelly H, Coyle P, Malek JA, Ahmed AA, Mohamoud YA, Younuskunju S, Ayoub HH, Al Kanaani Z, Al Kuwari E, Butt AA, Jeremijenko A, Kaleeckal AH, Latif AN, Shaik RM, Abdul Rahim HF, Nasrallah GK, Yassine HM, Al Kuwari MG, Al Romaihi HE, Al-Thani MH, Al Khal A, Bertollini R. SARS-CoV-2 antibody-positivity protects against reinfection for at least seven months with 95% efficacy. EClinicalMedicine. 2021 May;35:100861. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100861. Epub 2021 Apr 28. PMID: 33937733; PMCID: PMC8079668.
[40] Cohen KW, Linderman SL, Moodie Z, et al. Longitudinal analysis shows durable and broad immune memory after SARS-CoV-2 infection with persisting antibody responses and memory B and T cells. Cell Rep Med. 2021;2(7):100354. doi:10.1016/j.xcrm.2021.100354
[41] Nabin K. Shrestha, Patrick C. Burke, Amy S. Nowacki, Paul Terpeluk, Steven M. Gordon, Necessity of COVID-19 vaccination in previously infected individuals, medRxiv 2021.06.01.21258176; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.06.01.21258176
[42] Anderson DE, Tan CW, Chia WN, et al. Lack of cross-neutralization by SARS patient sera towards SARS-CoV-2. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2020;9(1):900-902. doi:10.1080/22221751.2020.1761267
[43] Meltzer DO, Best TJ, Zhang H, Vokes T, Arora V, Solway J. Association of Vitamin D Status and Other Clinical Characteristics With COVID-19 Test Results. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(9):e2019722. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.19722
[44] Meltzer DO, Best TJ, Zhang H, Vokes T, Arora VM, Solway J. Association of Vitamin D Levels, Race/Ethnicity, and Clinical Characteristics With COVID-19 Test Results. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(3):e214117. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.4117
[45] José L Hernández, Daniel Nan, Marta Fernandez-Ayala, Mayte García-Unzueta, Miguel A Hernández-Hernández, Marcos López-Hoyos, Pedro Muñoz-Cacho, José M Olmos, Manuel Gutiérrez-Cuadra, Juan J Ruiz-Cubillán, Javier Crespo, Víctor M Martínez-Taboada, Vitamin D Status in Hospitalized Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection, The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, Volume 106, Issue 3, March 2021, Pages e1343–e1353, https://doi.org/10.1210/clinem/dgaa733
[46] Shokri-Mashhadi N, Kazemi M, Saadat S, Moradi S. Effects of select dietary supplements on the prevention and treatment of viral respiratory tract infections: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2021 Apr 26:1-17. doi: 10.1080/17476348.2021.1918546. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 33858268.
[47] Pal, R., Banerjee, M., Bhadada, S.K. et al. Vitamin D supplementation and clinical outcomes in COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Endocrinol Invest (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-021-01614-4
[48] Jothimani D, Kailasam E, Danielraj S, Nallathambi B, Ramachandran H, Sekar P, Manoharan S, Ramani V, Narasimhan G, Kaliamoorthy I, Rela M. COVID-19: Poor outcomes in patients with zinc deficiency. Int J Infect Dis. 2020 Nov;100:343-349. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.014. Epub 2020 Sep 10. PMID: 32920234; PMCID: PMC7482607.
[49] Wenbo Wanga, Qianqian Lib,c, Jiajing Wub,d, Yu Hue,f, Gang Wua, Chuanfei Yua, Kangwei Xug, Xumei Liua,h,
Qihui Wang e, Weijin Huangb, Lan Wanga and Youchun Wang, Lentil lectin derived from Lens culinaris exhibit broad antiviral activities against SARS-CoV-2 variants, Emerging Microbes & Infections, 2021, VOL. 10, https://doi.org/10.1080/22221751.2021.1957720

This is excellent and up-to-the minute information, Donnie. Thank you for creating a narrative from disparate and current research that makes sense. My own instincts, followed over the course of my adult life , that natural adaptive immunity is to be nourished and respected hopefully will hold me in good stead. This and prayer, as I wait for Novavax. God bless you for putting in long hours to write this.
Thank you so very much
I’m very grateful to you for bringing together such a wide range of current research and information on Covid-19.
You are doing what the world needs more of right now.